Overview
Internet connections that are heavily utilized will experience call quality degradation and an overall poor experience with hosted voice. Like most hosted VoIP solutions, Primecall’s services work best with consistently low ping times and 60-90 kbps per concurrent phone call.
This document provides guidance for configuring a SonicWALL for Primecall services. Included are instructions for traffic prioritization. This uses features within the SonicWALL firewall to appropriately prioritize VoIP-related traffic above all other Internet traffic to help ensure a positive experience.
Subnet and Port Configuration
Primecall Public Subnets
- 199.71.209.0/24
- 24.227.249.0/25
- 72.249.136.32/28
- 206.123.122.32/27
- 212.69.157.32/27
- 40.143.31.64/27
Ports - Primecall Platform
- 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
- 20,000-40,000 UDP - RTP
- 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
- PrimecallMEETING - TCP and UDP
- 54.188.133.147:3443
- 3.130.158.184:3443
- 35.183.150.146:3443
- Text To Speech Services - TCP and UDP
- 54.149.243.27:8000
- 35.175.185.150:8000
- 54.149.243.27:3001
- 35.175.185.150:3001
- PrimecallWEB PHONE
- 9002 - TCP - websockets
- Portal Dynamic Updates
- 8001 - TCP
Ports - Enswitch 1 and 2 Platforms
- 5060-5062 UDP - SIP
- 10,000-20,000 UDP - RTP
- 80, 443 TCP - HTTP/HTTPS
Bandwidth Requirements
Voice-only applications utilize G.711 U-Law as the primary codec and require 87.2 kbps of bandwidth per active call.
It is recommended to round the requirement up to 100 kbps to account for signaling and overhead.
For Example… A 10Mbps/1Mbps ISP connection solely dedicated to the phones would support 10 concurrent phone calls.
VoIP Configuration
SonicOS includes the VoIP configuration settings on the VoIP → Settings page.
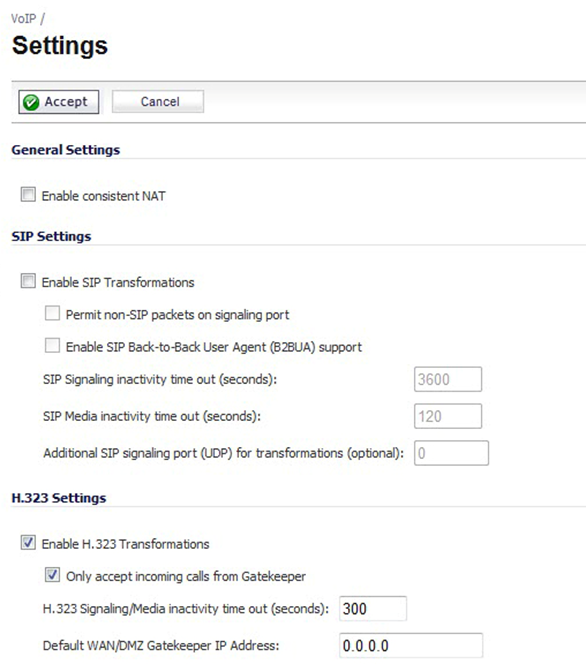
This page is divided into three configuration settings sections:
- General Settings
- SIP Settings
- H.323 Settings
General Settings
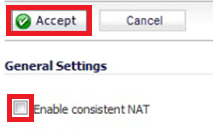
Enable Consistent NAT
To enable Consistent NAT, select Enable consistent NAT and click the Accept button. This option is disabled by default.
WARNING: Enabling Consistent NAT causes a slight decrease in overall security, because of the increased predictability of the address and port pairs. Most UDP-based applications are compatible with traditional NAT. Therefore, do not enable Consistent NAT unless your network uses applications that require it.
Consistent NAT enhances standard NAT policy to provide greater compatibility with peer-to-peer applications that require a consistent IP address to connect to, such as VoIP. Consistent NAT uses an MD5 hashing method to consistently assign the same mapped public IP address and UDP Port pair to each internal private IP address and port pair. Without Consistent NAT, the port and possibly the IP address change with every request.
For Example… NAT could translate the private (LAN) IP address and port pairs, 192.116.168.10/50650 and 192.116.168.20/50655 into public (WAN) IP/port pairs as follows:
| PRIVATE IP/PORT | TRANSLATED PUBLIC IP/PORT |
| 192.116.168.10/50650 | 64.41.140.167/40004 |
| 192.116.168.20/50655 | 64.41.140.167/40745 |
For this example, having Consistent NAT enabled ensures that all subsequent requests from either host 192.116.168.10 or 192.116.168.20 using ports 50650 and 50655 respectively will use the same translated address and port pairs for requests.
SIP Settings
SIP clients are VoIP devices that use SIP messaging to communicate, such as your Primecall desktop phones. SIP clients by default embed their private IP address in the SIP/Session Definition Protocol (SDP) messages to act as a return address for responses. These SIP and SDP messages are sent to a SIP proxy which processes and responds to the request.
If your SIP proxy is located on the public (WAN) side of the firewall and the SIP clients are on the LAN side, the SIP proxy does not know where to send SIP requests to SIP clients behind the firewall.
Enabling SIP Transformations allows the firewall to go through each SIP and SDP message and change the private IP address and assigned port to allow SIP and SDP messages transmitted between your LAN (trusted) and WAN/DMZ (untrusted) sides of your internet network. The Enable SIP Transformation setting also controls and opens up the RTP/RTCP ports that need to be opened for the SIP session calls to happen. NAT translates Layer 3 addresses but not the Layer 7 SIP/SDP addresses, which is why you need to select Enable SIP Transformations to transform the SIP messages.
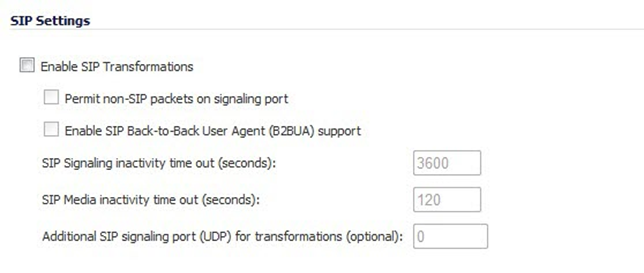
Note: In general, you should check the Enable SIP Transformations box unless there is another NAT traversal solution that requires this feature to be turned off. SIP Transformations works in bi-directional mode, meaning messages are transformed going from LAN to WAN and vice versa.
Permit Non-SIP Packets on Signaling Port
Selecting Permit non-SIP packets on signaling port enables applications, such as Apple iChat and MSN Messenger, to use the SIP signaling port for additional proprietary messages. This checkbox is disabled by default.
DANGER: Enabling this setting may open your network to malicious attacks caused by malformed or invalid SIP traffic.
Enable SIP Back-to-Back User Agent (B2BUA) Support
The Enable SIP Back-to-Back User Agent (B2BUA) Support setting should be enabled when the firewall can see both legs of a voice call (for example, when a phone on the LAN calls another phone on the LAN). This setting should only be enabled when the SIP Proxy Server is being used as a B2BUA.
Note: If there is no possibility of the firewall seeing both legs of voice calls (for example, when calls will only be made to and received from phones on the WAN), the Enable SIP Back-to-Back User Agent (B2BUA) support setting should be disabled to avoid unnecessary CPU usage.
SIP Signaling and Media Inactivity Time Outs
SIP Signaling inactivity time out (seconds) and SIP Media inactivity time out (seconds) define the amount of time a call can be idle (no traffic exchanged) before the firewall blocks further traffic. A call goes idle when placed on hold.
Quick Tip: The default time value for SIP Signaling inactivity time out is 1800 seconds (30 minutes). The default time value for SIP Media inactivity time out is 120 seconds (2 minutes).
Additional SIP Signaling Port (UDP) for Transformations
The Additional SIP signaling port (UDP) for transformations setting allows you to specify a non-standard UDP port used to carry SIP signaling traffic. Normally, SIP signaling traffic is carried on UDP port 5060. However, a number of commercial VOIP services use different ports, such as 1560. Using this setting, the security appliance performs SIP transformation on these non-standard ports.
H.323 Settings
Select Enable H.323 Transformation in the H.323 Settings section and click Accept to allow stateful H.323 protocol-aware packet content inspection and modification by the firewall. Disable the Enable H.323 Transformation to bypass the H.323 specific processing performed by the firewall.
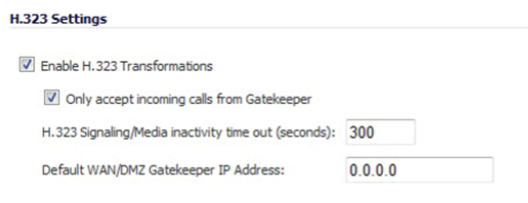
✔ When H.323 transformations are enabled, the firewall performs any dynamic IP address and transport port mapping within the H.323 packets. This function is necessary for communication between H.323 parties in trusted and untrusted networks/zones.
Only Accept Incoming Calls from Gatekeeper
Select Only accept incoming calls from Gatekeeper to ensure all incoming calls go through the Gatekeeper for authentication.
✔ The Gatekeeper will refuse calls that fail authentication.
H.323 Signaling/Media Inactivity Time Out
The H.323 Signaling/Media inactivity time out (seconds) field specifies the amount of time a call can be idle before the firewall blocks further traffic.
Note: A call goes idle when placed on hold while on an active call, parked in a park queue, or waiting in a call queue.
The default time value for H.323 Signaling/Media inactivity time out is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
Default WAN/DMZ Gatekeeper IP Address
The Default WAN/DMZ Gatekeeper IP Address field has a default value of 0.0.0.0. Enter the default H.323 Gatekeeper IP address in this field to allow LAN-based H.323 devices to discover the Gatekeeper using the multicast address 225.0.1.41.
NOTE: If you do not enter an IP address, multicast discovery messages from LAN-based H.323 devices will go through the configured multicast handling.
Configure BWM and QoS
One of the greatest challenges for VoIP is ensuring high speech quality over an IP network. IP was designed primarily for asynchronous data traffic, which can tolerate delay. In contrast, VoIP and other types of media streaming are very sensitive to delay and packet loss. Managing access and prioritizing traffic are important requirements for ensuring high-quality, real-time VoIP communications.
✔ SonicWALL have integrated Bandwidth Management (BWM) and Quality of Service (QoS) features that provide tools for managing the reliability and quality of your VoIP communications.
Quality of Service
QoS encompasses a number of methods intended to provide predictable network behavior and performance. Network predictability is vital to VoIP and other mission-critical applications. No amount of bandwidth can provide this sort of predictability, because any amount of bandwidth will ultimately be used to its capacity at some point in a network. Only QoS, when configured and implemented correctly, can properly manage traffic and guarantee the desired levels of network service.
✔ SonicOS includes QoS features that add the ability to recognize, map, modify and generate the industry-standard 802.1p and Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCP) Class of Service (CoS) designators.
Manage Bandwidth on the WAN Interface
Egress and Ingress BWM can be enabled jointly or separately on WAN interfaces. Different bandwidth values may be entered for outbound and inbound bandwidth to support asymmetric links. Link rates up to 100,000 Kbps (100Mbit) may be declared on the Fast Ethernet interface, while Gigabit Ethernet interfaces will support link rates up to 1,000,000 (Gigabit).
WARNING: The bandwidth specified should reflect the actual bandwidth available for the link. Oversubscribing the link (declaring a value greater than the available bandwidth) is not recommended.
Set Up Bandwidth Management
Once one or both BWM settings are enabled on the WAN interface and the available bandwidth has been declared, a Bandwidth tab will appear on Access Rules.
To configure Bandwidth Management on your SonicWALL…
- Navigate to Network → Interfaces.
- Click the Edit icon in the Configure column in the WAN (X1) line of the Interfaces table.
- In the Edit Interface window, the Advanced tab.
- Select Enable Egress (Outbound) Bandwidth Management and enter the available bandwidth in the Available Interface Egress Bandwidth Management field.
- Select Enable Ingress (Inbound) Bandwidth Management and enter the available bandwidth in the Available Interface Ingress Bandwidth Management field.
- Click OK.
Configure VoIP Access Rules
By default, stateful packet inspection on your firewall allows all communication from the LAN to the Internet and blocks all traffic to the LAN from the Internet. Additional network access rules can be defined to extend or override the default access rules.
If you are defining VoIP access for a client to use a VoIP service provider from the WAN, you configure network access rules between source and destination interface or zones to enable clients behind the firewall to send and receive VoIP calls.
Quick Tip: Although custom rules can be created that allow inbound IP traffic, the firewall does not disable protection from Denial-of-Service attacks, such as the SYN Flood and Ping of Death attacks.
NOTE: You must select Bandwidth Management on the Network → Interfaces page for the WAN interface before you can configure bandwidth management for network access rules.
Create Access Rules for VoIP Traffic
- Navigate to Firewall → Access Rules.
- For View Style, click All Rules.
- Click Add at the bottom of the Access Rules table. The Add Rule window is displayed.
- In the General tab, select Allow from the Action list to permit traffic.
- Select the from and to zones from the From Zone and To Zone menus.
- Select the service or group of services affected by the access rule from the Service list:
- For H.323, select one of the following or select Create New Group and add the following services to the group:
- H.323 Call Signaling
- H.323 Gatekeeper Discovery
- H.323 Gatekeeper RAS
- For SIP, select SIP
- For H.323, select one of the following or select Create New Group and add the following services to the group:
- Select the source of the traffic affected by the access rule from the Source list. Selecting Create New Network displays the Add Address Object window.
- If you want to define the source IP addresses that are affected by the access rule, such as restricting certain users from accessing the Internet, select Range in the Type: drop-down menu. Then enter the lowest and highest IP addresses in the range in the g IP Address: and Ending IP Address fields.
- Select the destination of the traffic affected by the access rule from the Destination list. Selecting Create New Network displays the Add Address Object window.
- From the Users Allowed menu, add the user or user group affected by the access rule.
- Select a schedule from the Schedule menu if you want to allow VoIP access only during specified times. The default schedule is Always on. You can specify schedule objects on the system > Schedules page.
- Enter any comments to help identify the access rule in the Comments field. (ie. “VoIP”)
- Click the Bandwidth tab.
- Select Bandwidth Management, and enter the Guaranteed Bandwidth in Kbps.
- Enter the maximum amount of bandwidth available to the Rule at any time in the Maximum Bandwidth field.
- Assign a priority from 0 (highest) to 7 (lowest) in the Bandwidth Priority list. For higher VoIP call quality, ensure VoIP traffic receives HIGH priority.
Quick Tip: Rules using Bandwidth Management take priority over rules without bandwidth management.
Enable VoIP Logging
You can enable the logging of VoIP events on the Log → Settings page. Log entries are displayed on the Log → Monitor page. To enable logging of VoIP, see Log → Settings.